Stop Breathing While Sleeping
What is it Called When People Stop Breathing in Sleep?
Many people snore in their sleep.
However, some snorers actually stop breathing while sleeping for 30 or more seconds, several times during the night.
This condition is called obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a life-threatening sleep breathing disorder, and has the following signs:
- loud, irregular and repeated snoring,
- feeling tired during the day, and taking naps.
In addition obstructive apnea, there is another type of apnea syndrome called central sleep apnea.
By contrast, a person with central apnea doesn't make any sound while sleeping. He just stops breathing because the brain forgets to send breathing signals for a couple of seconds.
For more info about obstructive apnea signs, see Symptoms of Sleep Apnea.
Sleep Apnea Definition - 10 seconds or more
Many healthy people stop breathing while sleeping for a second or two.
However, when a person stops breathing during sleep for more than 10 seconds, the situation is abnormal and becomes an apnea episode, also called:
- apnea,
- apnea event
- breath cessation.
When Doctors Say It's Sleep Apnea?
Doctors will diagnose a patient with sleep apnea if he has at least 35 apnea episodes per night, or more than 5 per hour of sleep, each lasting 10 seconds or longer.
The Sound When Breathing Stops While Sleeping
At the beginning of this video you will actually see and hear when a patient stopped breathing while sleeping. If you have obstructive sleep apnea, you will understand how do you sound in sleep:
How Long do People Stop Breathing While Sleeping?
Severe sleep apnea patients can stop breathing during sleep for up to almost 2 minutes! After this pause, he briefly wakes up gasping and snorting for air, without knowing it.
"He doesn't believe his breathing stops when sleeping"
People with sleep apnea wake up from sleep to breathe, but they don't realize that they have awakened.
They just gasp for air and they fall asleep again like nothing happened. Only the bed partner can see these scary awakenings.
The same phenomenon happens with snoring: have you ever listen to yourself snoring? It's very rare when you can hear that.
Some of the patients with sleep apnea wake up during sleep and think they have another problem, such as insomnia or nightmares. Others will think that they are just fine with their sleep and they get mad when someone tells them to stop snoring.
If you know such a person, a good idea is to video-record him with an infrared camera when he's asleep. He might cool down and take measures when he will see how he's breathing stops in sleep for such a long period of time.
There is one more problem in people with sleep apnea: they stop breathing in sleep more than once! In fact, they have many apnea episode, like 200 times per night, and even 900 times per night in most severe cases!
Now, try to stop breathing for 60 seconds (if you can...), then breathe normally for 60 seconds, and hold your breath for another 60 seconds. Can you do this 200 times? Imagine how would you feel in the morning after a full night of apnea events:
- excessive fatigue,
- morning headaches,
- taking naps often during the day,
- falling asleep while driving, etc.
For more info about the health problems from sleep apnea, see Sleep Apnea Side Effects.
Why do Apnea Patients Wake Up after they Stop Breathing?
Your brain knows that if you stop breathing for more than 2 or 3 minutes and you don't start to breathe again, you can die.
These awakening episodes will save your life, but they do disturb your sleep and cause excessive daytime sleepiness.
Unfortunately, sleep apnea can cause so much damage to your body that some people can even die from it.
For more info about death from sleep apnea, see Sleep Apnea Death.
Why do People Stop Breathing While Sleeping?
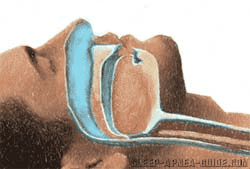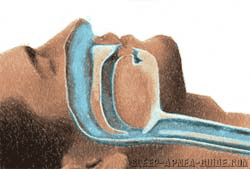
The upper pharyngeal airway (the tube from your throat) has 2 purposes:
- to swallow the food
- and to breathe.
When used for swallowing, the pharynx has to be relaxed to carry the food. When used for breathing, it has to remain an open and rigid tube like the trachea.
These functions are possible only by having floppy and collapsible muscular tube that is also capable of being held open rigidly by dilator muscles.
However, during sleep, all these muscles relax, so we do normally have some pharyngeal narrowing.
Some people start to snore if the airway is too narrow.
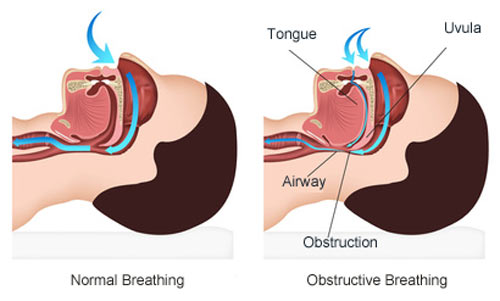
In obstructive apnea, the pharyngeal airway collapses during sleep until is blocking the airway completely.
The are two main causes for these collapses:
- the pharyngeal dilator muscles relaxes too much during sleep,
- or there may be anatomical abnormalities.
Here are some examples of anatomical abnormalities:
- large tongue,
- short neck,
- large uvula,
- receding jaw,
- deviated septum,
- nasal polyps,
- allergies,
- swollen tonsils or adenoids, etc.
How Do You Know if You Stop Breathing While Sleeping?
Most often the bed partner is the one who triggers the alarm. He or she reports loud snoring, breathing interruptions, or both during your sleep.
A sleep study is necessary to discover if you really have sleep apnea, or other sleep disorders, how severe is it, and the most effective treatment.
Sometimes you can diagnose sleep apnea at home; however, only a sleep study can confirm this.
More strategies for diagnosing sleep apnea:
- Diagnosing Sleep Apnea at Home
- Complete a simple questionnaire to discover if you have OSA
- Simple OSA diagnosis with sound recording
Treatments for Sleep Apnea
Fortunately, there are many options to treat sleep apnea, from the most effective but expensive ones, to alternative solutions:
Treating OSA with Special Exercises
If your throat muscles relax too much during sleep causing obstructive apnea, you can stiffen those muscles with special exercises.
These exercises were clinical tested with success in mild cases of OSA, but can also improve moderate cases, too.
Bottom line... Most of the time you will not remember stop breathing while sleeping. In this case, your bed partner is maybe your only hope in saving your life and your relationship.

Sleep Apnea › Symptoms of Sleep Apnea › Stop Breathing While Sleeping