Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome
Differences Between UARS and Sleep Apnea
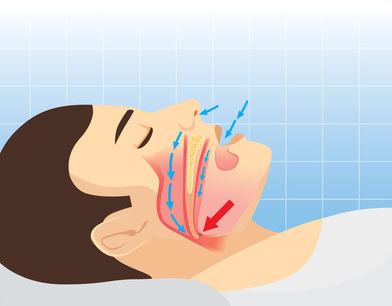
In this article you'll discover the differences and similarities between upper airway resistance syndrome (UARS) and obstructive sleep apnea.
You'll also learn how to diagnose UARS, what are the causes and how can it be treated.
What is UARS?
Did you know that you could suffer from a sleep breathing disorder without a single apnea or hypopnea?
The upper airway resistance disorder is a type of sleep breathing disorder associated with arousals from sleep. Sometimes called respiratory effort-related arousals (RERAs), this syndrome is difficult to diagnose even in sleep centers.
In other words, with upper airway resistance syndrome, your airway closes, but before you actually stop your brain realizes you're having trouble breathing, and you slightly wake up (arouse) to take a deeper breath and keep yourself from stopping breathing altogether.
Symptoms of Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome
The most common symptoms of UARS are very similar to sleep apnea, but they are key differences that are difficult to be recognize without a sleep study:
- frequent sleep arousals (sleep fragmentation),
- daytime sleepiness and fatigue,
- there are increasing efforts to breathe during sleep, but you don't stop breathing,
- there are no apnea episodes (stop breathing in sleep), only arousals (you wake up),
- minimal or no oxygen desaturation (greater than 90%),
- headaches,
- complain of insomnia,
- depression,
- cold hands or feet,
- gastrointestinal problems,
- attention deficit disorders.
Bottom line... UARS doesn't usually cause the problems that come from lack of oxygen (like high blood pressure and heart problems), but does cause the problems that come with lack of sleep (like fatigue, sleepiness, low glucose tolerance, depressed immune system, etc.) because the arousals are as frequent as they would be with apnea.
Causes of UARS
The upper airway resistance syndrome is apparently the most simple form of sleep disordered breathing. Many people with UARS also experience snoring or apnea episodes.
The cause of this syndrome is not clear even today, but the fact that the majority of people in whom UARS was found have a narrowing of the airways, indicates that the cause is linked to a minor airflow disruption due to the structure of the airways.
Differences between UARS and Sleep Apnea
With obstructive sleep apnea, you have a cessation of breathing. So, when your airways close while sleeping, you stop breathing, and after a couple of seconds your body realizes you had stopped breathing and you'll wake up to breathe again.
However, with UARS, you are waking up right before you would have had an apnea episode (before you stop breathing in sleep).
This video explains more about the differences between sleep apnea and UARS:
How to Diagnose UARS?
Although UARS and sleep apnea are related to excessive daytime sleepiness and depressive mood, recognition of UARS is complicated because it's not detected by standard nocturnal polysomnography.
With a polysomnograph, the sleep doctor can detect on the graphic when and how did you stop breathing in sleep. However, in UARS there is no apnea episodes, so the graphics cannot be helpful for diagnosing.
The only way to diagnose the syndrome is by monitoring pressure variations in the thorax during sleep, and this is done with nocturnal esophageal manometry, or esophageal balloon manometry, which is a technique reflecting the inspiratory efforts as negative pressure.
But this method is not well tolerated by every patient, and there is need for extra equipment and expertise to accurate diagnose UARS.
UARS Treatment
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure - CPAP
Since the physical cause of UARS is the same with obstructive sleep apnea (narrowing of the airway during sleep), both sleep disorders are treated with CPAP.
Even with a low pressure from your CPAP machine, the MSLT can show improvements in your sleep.
Unfortunately, UARS patients don't tolerate CPAP very well, because these patients are very sensible, whereas OSA patients have a relatively diminished nervous system. This is why sleep apnea patients stop breathing for so long, and UARS wake up so quickly.
Waking up from every little sound, light or movement leads to a physiological stress response that can lead to various hormonal changes in your body, in your nervous system, in your immune system (leading to various autoimmune conditions).
Special Oral Appliances

Oral appliances can also help you treat UARS, but don't count on it to cure your upper airway resistance without testing in the sleep center.
Insurance Problems for UARS Treatment
There is another issue that can affect the treatment of UARS: this syndrome is not recognized by many insurance companies, including Medicare.
Furthermore, some sleep doctors will not test for upper airway resistance syndrome because of their frustration in dealing with these insurance companies, which prevent prescribing appropriate treatment.
Bottom line... Some insurance companies will not pay for patients to use CPAP therapy if they suffer only from upper airway resistance syndrome.
Home › Sleep Disorders › Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome